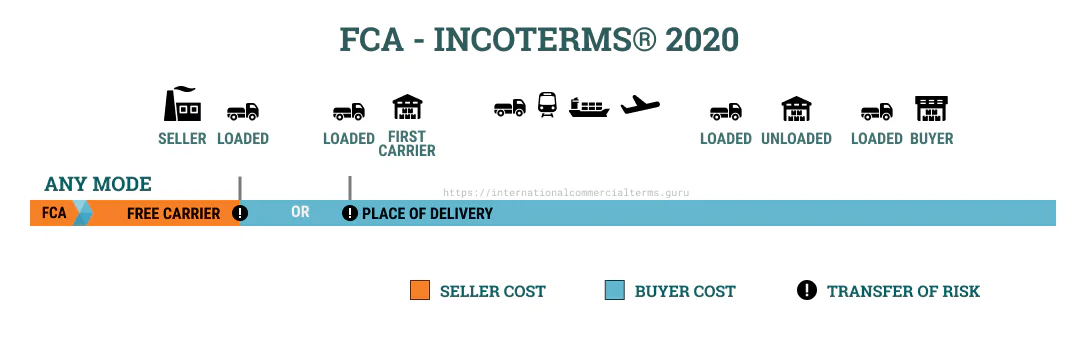
FCA
Free Carrier (Place of Delivery)
Explained
In the event that the delivery location is at the seller’s premises, it is the responsibility of the seller to load the goods. In the event that delivery is made to a location other than the seller’s premises, the seller shall not be held responsible for unloading.
In this context, the term “carrier” refers to any party responsible for the contract of carriage and tasked with transporting the goods by any mode of transportation.
There are two possible locations for receipt under an FCA: the seller’s facility or another location, typically a freight forwarder’s facility or a port or airport terminal. It is the responsibility of the seller to load goods into a transport vehicle (arranged by the buyer) only when the place of receipt is the seller’s facility.
In accordance with the Incoterms® 2020 standard, the buyer has the option to instruct the carrier to issue a bill of lading with an “onboard” notation when the place of delivery is an inland point. The seller is required to provide the buyer with the relevant documentation, which must include the same clauses as outlined in the contract. It should be noted that the seller is not obliged to include any particular clauses in the contract.
It is the responsibility of the seller to clear customs for exports. International freight and transport arrangements must be made by the buyer.
Doing Business
In the event that the specified location is not the seller’s facility, the seller is not obliged to unload the goods, as it is assumed that the receiving facility has the necessary resources to do so (i.e., a warehouse freight station for LCL cargo or a container terminal).
FCA can be used for any mode of transportation or a combination of modes (multimodal). It is recommended that the buyer clearly specify the place of delivery. As an example, the address could be “Kuehne and Nagel - East Shanghai Road No.5 Room 1103, Huaqiao Mansion, 215400 Suzhou City” is a more explicit address than “Kuehne and Nagel Shanghai Warehouse.”
FCA is an optimal choice for buyers seeking to maintain control over costs at the origin and for international transportation through a nominated freight forwarder. FCA is frequently used in conjunction with a Forwarder Cargo Receipt (FCR), a document that serves to verify that cargo has been received by a forwarder with the intention of being transported in accordance with the buyer’s specified conditions. A FCR serves as proof of delivery and can be used in lieu of a bill of lading for document compliance purposes.
In the case of FCA, the buyer is responsible for covering the cost of origin terminal handling charges when the cargo is containerized. In this context, the term “carrier” refers to any company that has been appointed by the buyer to act as a transport agent. In such cases, a freight forwarder can also be considered a carrier.
It is advisable to opt for FCA over FOB for containerized cargo. In the case of FCL, the container can be placed at the seller’s facility. In the event that the cargo is to be transported as LCL, it is typically required that the seller deliver the goods into a nominated warehouse for consolidation.
Carriers clauses
There are various types of carriers that could be engaged to facilitate delivery. An inland carrier for road transportation, a freight forwarder for multimodal transportation, an airline, a rail transport company, or a shipping line. In the case of ocean shipments, the term “on board” is typically used to indicate that the goods are on the vessel. In the event that the bill of lading is issued prior to on-board shipment, the carrier (freight forwarder) is permitted to indicate “received for shipment.”
Examples
At sellers facility (shipper must load cargo into container):
FCA ABB - 1133 South Cavalier Drive, Alamo USA - Incoterms® 2020At forwarders facility (buyer pays for unloading cost):
FCA Panalpina World Transport
6/F AZIA Center, 1233 Lujiazui, Ring Road
Pudong New Area, Shanghai 200120, China
Incoterms® 2020At the airport:
FCA KLM - Menzies World BV, Brandenburgbaan 2b, 3045 AK Rotterdam - Incoterms 2020Seller and Buyer obligations
| THE SELLER’S OBLIGATIONS | THE BUYER’S OBLIGATIONS |
|---|---|
| A1. General The seller must deliver the goods, commercial invoice, and evidence of conformity | B1. General The buyer must pay the price of goods as agreed in the contract of sale |
| A2. Delivery Deliver the goods at the agreed point, date or period. If no time is notified, when goods have been loaded or placed at disposal of the carrier | B2. Taking Delivery The buyer takes the goods after delivered in the agreed time. |
| A3. Risks All risk of loss/damage until goods have been delivered | B3. Risks All risk of loss/damage from the time or end of the period agreed for delivery. If the buyer fails to nominate a carrier, or if the carrier doesn’t pick up the goods, the risk is under the buyer. |
| A4. Carriage No obligation to make a contract of carriage. Provide at buyers risk and cost, information for arranging carriage. If agreed, the seller must contact the carrier. | B4. Carriage Contract the carriage from the place of delivery unless agreed with the seller. |
| A5. Insurance No obligation. Provide at buyers risk and cost, any required information. | B5. Insurance No obligation to insure the goods. |
| A6. Delivery/transport document Proof of delivery at sellers cost and a transport document if arranged by seller | B6. Delivery/transport document Accepts the proof of delivery. If agreed the buyer must instruct the carrier to issue a transport document. |
| A7. Export/Import clearance All export clearance expenses (license, security, inspection, etc). Assist with import clearance | BB7. Export/Import clearance Assist with export clearance. Import clearance and formalities (licenses, security, official documentation). |
| A8. Checking The seller must check, count, weight, mark, and package goods | B8. Checking No obligation. |
| A9. Allocation of cost Pay all the cost until delivery. Cost of proof of delivery. Duties and taxes for export. All costs related to providing assistance in obtaining documents to the buyer | B9. Allocation of cost Pay from the time goods delivered. All costs for assistance on getting carriage, insurance, delivery, and customs documentation. Pay duties and taxes for import or transit. Any additional cost if the carrier is not nominated or carrier fails to collect goods. |
| A10. Notices Give notice that goods have been delivered or failed to be collected by carrier. | B10. Notices Notify the carrier nominated, time or period, mode fo transportation and the point where goods will be received. |
FAQ about FCA
How does FCA differ from FOB?
They are fundamentally different:
FCA:
- Appropriate for ANY mode of transport
- Recommended for containerized cargo
- Delivery when seller physically hands over goods to the buyer’s carrier
- Two options in Article A2 for delivery point
FOB:
- Only for sea or inland waterway transport
- Only for bulk/breakbulk (NOT containers)
- Delivery when goods pass ship’s rail / are on board vessel
- Seller’s risk passes when goods are shipped on board
For containers: Always use FCA, never FOB.
How does FCA work with export customs clearance?
Under FCA, the seller is responsible for export clearance. However, in practice, sellers may give the export clearance responsibility to the buyer’s forwarder/carrier.
EU-specific challenges:
- The exporter of record remains fully liable for VAT owed for 10 years under updated EU customs laws (effective 2017)
- The seller must be able to provide full documentation covering the export
- If the buyer’s carrier handles the export declaration, the seller has zero control and cannot verify if it’s done properly
Expert insight: FCA doesn’t fit well with AEO (Authorized Economic Operator) requirements, where the exporter must have some degree of control over subcontractors. If the seller wants to minimize risk of not receiving confirmation of exit, they should choose a C or D term instead.
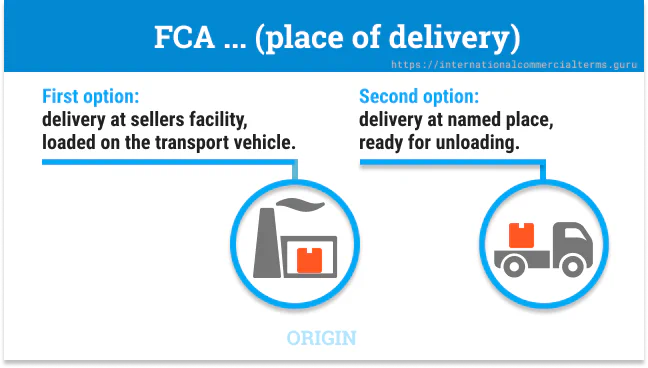
What are the two delivery options under FCA?
Option (a) - Seller’s premises:
- For FCL: Seller loads goods into the container
- For LCL: Seller loads goods onto the collecting vehicle
- Delivery when goods are loaded
Option (b) - Carrier’s place:
- Seller transports goods to carrier’s depot/terminal/warehouse
- Delivery when seller’s vehicle arrives ready for unloading by the carrier
- Commonly used for LCL and air freight
- When used in FCL, the carrier’s terminal should be clearly specified