Title here
Summary here
In DPU, the seller is responsible for moving goods from origin to destination. The seller is responsible for the goods until they reach the agreed delivery point. This term can be used for any mode of transportation. The seller must arrange for the goods to be unloaded at the agreed-upon place.
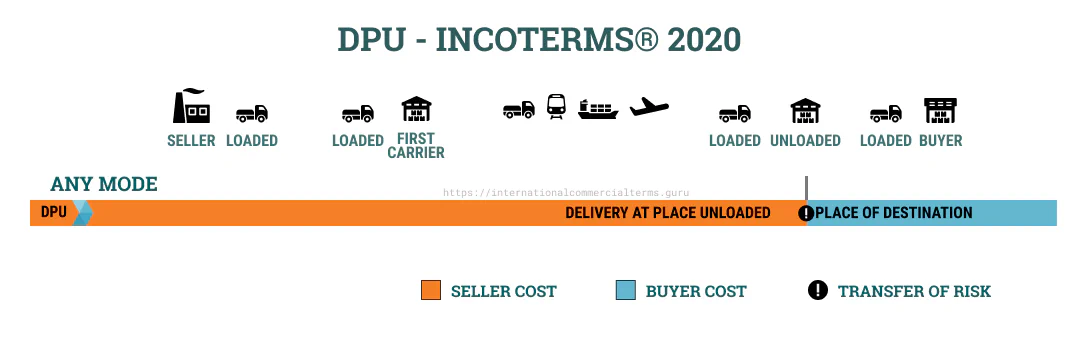
The seller is responsible for unloading goods at the destination. The seller can unload the goods at a port, warehouse, or transshipment point.
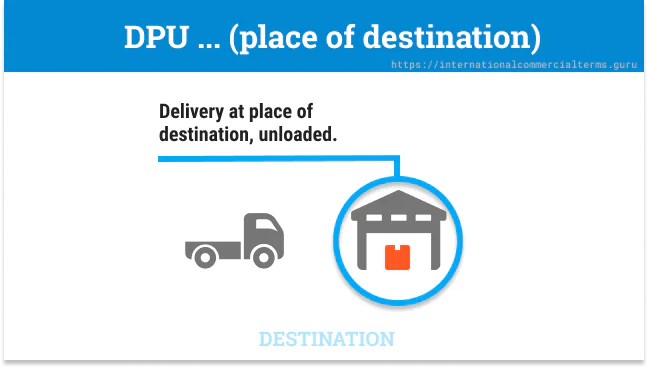
Ocean Cargo:
DPU Singapore Port, Pier 10, Singapore - Incoterms® 2020Air Cargo:
DPU Swissport terminal, Frankfurt, Germany - Incoterms® 2020| THE SELLER’S OBLIGATIONS | THE BUYER’S OBLIGATIONS |
|---|---|
| A1. General: the seller must deliver the goods, commercial invoice, and any evidence of conformity. | B1. General: the buyer must pay the price of goods as agreed. |
| A2. Delivery Deliver the goods at the disposal of the buyer, unloaded. On the agreed date or period. | B2. Taking Delivery The buyer takes the goods at the destination point. |
| A3. Risks All risk of loss/damage until goods have been delivered. | B3. Risks All risk of loss/damage from the time or end of the period agreed for delivery. If the buyer fails to clear import customs or notify time/period, the risk is under the buyer. |
| A4. Carriage Contract carriage of goods until the place of destination. | B4. Carriage No obligation to contract a carrier. |
| A5. Insurance No obligation. | B5. Insurance No obligation to insure the goods. |
| A6. Delivery/transport document Provide documents that allow the buyer to take over the goods. | B6. Delivery/transport document Accepts the proof of delivery |
| A7. Export/Import clearance All export clearance expenses (license, security, inspection, etc). Assist with import clearance | B7. Export/Import clearance Assist with export clearance. Pay for import clearance and formalities (licenses, security, official documentation). |
| A8. Checking The seller must check, count, weight, mark, and package goods | B8. Checking No obligation. |
| A9. Allocation of cost Pay all the cost until delivery. Transport and loading. Unloading charges. Transit costs. Cost of delivery/transport document. Duties and taxes for export. All costs related to providing assistance in obtaining documents to the buyer. | B9. Allocation of cost Pay from the time goods delivered. All costs for assistance. Pay duties and taxes for imports. Any additional cost if does not notify the shipment date or period. |
| A10. Notices Give the notice to receive the goods. | B10. Notices Time or period for receiving the goods and name the point of receiving the goods. |