Incoterms 2020
International Commercial Terms Rules
The Incoterms® rules or International Commercial terms are a series of pre-defined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC) widely used in international commercial transactions. A series of three-letter trade terms related to common sales practices, the Incoterms rules are intended primarily to clearly communicate the tasks, costs and risks associated with the transportation and delivery of goods. The Incoterms rules are accepted by governments, legal authorities and practitioners worldwide for the interpretation of most commonly used terms in international trade. They are intended to reduce or remove altogether uncertainties arising from different interpretation of the rules in different countries. First published in 1936, the Incoterms rules have been periodically updated, with the eighth version—Incoterms 2010—having been published on January 1, 2011. “Incoterms” is a registered trademark of the ICC.
Incoterms 2020
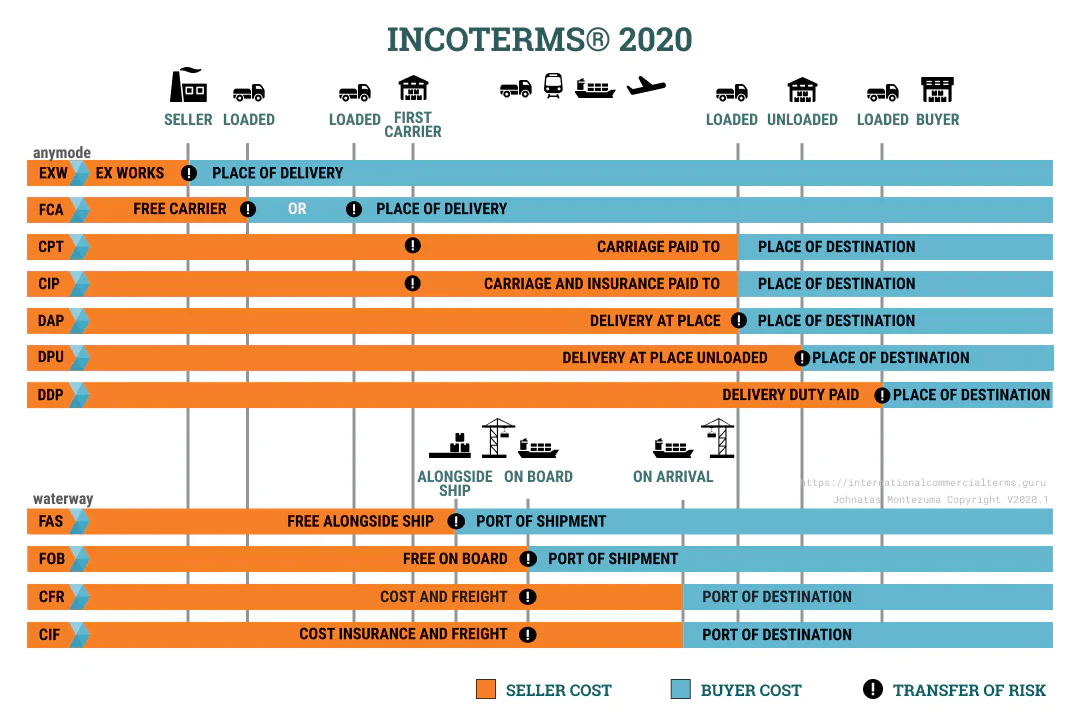
Incoterms 2020 main changes
- DAT term changed to DPU (Delivery at Place unloaded)
- FCA has two possible options
- CIP requires insurance clause A instead of C
- A new section of cost has been included
- Customs clearance with export, transit and import explanations
- FCA with a Bill of Lading on board notification if agreed
Incoterms in Government Regulations
In certain jurisdictions, the duty costs of the goods may be calculated based on a specific term. For instance, in India, duty is calculated against the CIF (Cost, Insurance, Freight) value of the goods, while in South Africa, the duty is calculated against the FOB (Free On Board) value of the goods. As a result, it is common practice for contracts for exports to these countries to utilise these Incoterms, even when they are not aligned with the selected mode of transportation. It is essential to exercise caution to ensure that liability issues are addressed through negotiation with the customer.
Incoterms and the exporter
International Commercial Terms, otherwise known as “Incoterms,” are internationally accepted terms that define the responsibilities of exporters and importers in the arrangement of shipments and the transfer of liability involved at various stages of the transaction. It should be noted that the Incoterms do not cover the issue of ownership or the transfer of title of the goods in question. It is of the utmost importance to reach an agreement on a term at the outset of a negotiation or quotation of a sale, as it will have a significant impact on the costs and responsibilities involved in shipping, insurance, and tariffs. The new Incoterms 2010 rules were revised by the International Chamber of Commerce and became effective on January 1, 2011.
In any sales transaction, it is of the utmost importance for the seller and buyer to agree on the terms of sale and to have a clear understanding of what is included in the sale price. Exporters should select the term that is most advantageous for their company, but they should also be prepared to quote on other Incoterms.
Shipping
Once the purchase has been completed, the goods must be delivered and transported to the buyer. This process necessitates the following:
Proof of delivery by the supplier, indicating that the goods are in good order
Risk management through insurance
An appropriate package or container for full container loads (FCL)
Provision of shipping instructions to shippers
Receipt of all necessary documentation from the seller for export and import goods