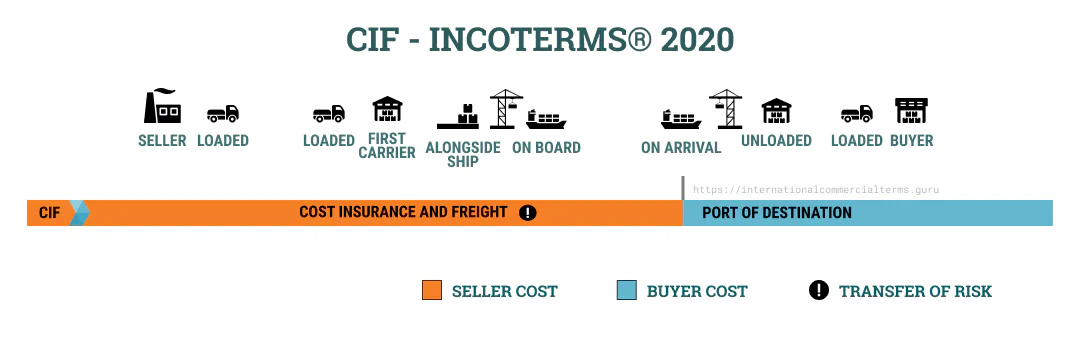
CIF
Cost, Insurance and Freight paid to (Port of Destination)
Explained
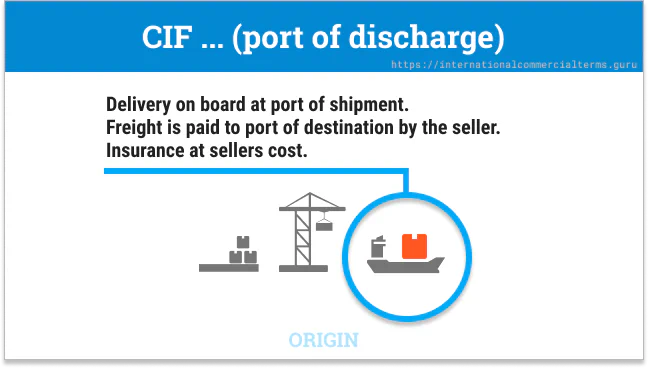
In CIF terms, the seller pays for insurance until the goods reach the port of discharge. The seller pays for insurance during transport, but the buyer is responsible for the goods once they are on board. This term is for ocean and inland waterway transportation.
Doing Business
The seller is insured until the goods reach their destination. The seller must also arrange international shipping and provide the buyer with all the necessary documents. The seller must also clear customs. This term is only used for ocean transportation. If cargo doesn’t fit a container, use CIT. This term is used for agricultural or chemical products where the seller can arrange loading and transportation until the port of discharge and insurance.
This term is used for bulk cargo, oil, and oversized items. The buyer pays for unloading.
Insurance must cover the price of goods plus 10%.
Examples
Buying scrap metal from Thailand (scrap metal also gets insured):
CIF Shanghai Port, China - Incoterms® 2020Seller and Buyer obligations
| THE SELLER’S OBLIGATIONS | THE BUYER’S OBLIGATIONS |
|---|---|
| A1. General The seller must deliver the goods, commercial invoice, and any evidence of conformity. | B1. General The buyer must pay the price of goods as agreed. |
| A2. Delivery Deliver the goods by placing on board the vessel in the agreed date or period. In a customary manner at the port | B2. Taking Delivery The buyer takes the goods from the carrier at the port of destination |
| A3. Risks All risk of loss/damage until goods have been delivered | B3. Risks All risk of loss/damage from the time or end of the period agreed for delivery. If the buyer fails to give notice of the port of destination, the risk is under the buyer. |
| A4. Carriage Contract carriage of goods until port of destination. | B4. Carriage No obligation to contract a carrier. |
| A5. Insurance The seller must obtain cargo insurance. Additional insurance coverage under the buyer account. | B5. Insurance No obligation to insure the goods. |
| A6. Delivery/transport document Provide the usual transport document. | B6. Delivery/transport document Accepts the proof of delivery |
| A7. Export/Import clearance All export clearance expenses (license, security, inspection, etc). Assist with import clearance | B7. Export/Import clearance Assist with export clearance. Pay for import clearance and formalities (licenses, security, official documentation). |
| A8. Checking The seller must check, count, weight, mark, and package goods | B8. Checking No obligation. |
| A9. Allocation of cost Pay all the cost until delivery, freight cost, and loading cost. Unloading cost if agreed in the contract. Transit costs. Cost of proof of delivery. Insurance. Duties and taxes for export. All costs related to providing assistance in obtaining documents to the buyer | B9. Allocation of cost Pay from the time goods delivered. All costs for assistance on getting carriage, delivery, and customs documentation. Pay duties and taxes for import or transit. Any additional cost if the carrier is not nominated or carrier fails to collect goods. |
| A10. Notices Give notice that goods have been delivered on board. | B10. Notices Time or period for receiving the goods and name the port of destination. |
FAQ about CIF
Why does the seller pay for transport under CFR but the buyer bears the risk?
A similar answer applies to CIF as to CFR.
This reflects historical practice from the 1800s. CFR (via its predecessor C&F) pre-dates the first set of Incoterms rules.
Historical context: Imagine in the 1800s, a seller contracts with a ship-owner to transport goods from A to B but doesn’t want marine risks while goods are on the high seas. The seller (likely already paid in cash before shipment) agrees to load goods onto the ship and pay the freight, but not bear the ocean risk.
Modern reality: The confusion often comes from the word “responsibility,” which is interpreted as including risk. Incoterms never use this word. Under CFR/CIF:
- Seller must pay the freight
- Buyer bears all risks of loss/damage once goods are loaded on board in the port of shipment
- Depending on the buying power of buyer/seller, the party with more power to get ocean freight rates often negotiates who pays for freight
- Example: a large mobile distributor selling to small retailers may have the leverage to negotiate better ocean freight rates than the small retailers. In this case, the large distributor may agree to pay for freight (CFR/CIF) even though the small retailers bear the risk. The ocean freight contract is under the Seller’s name and bill of ladings are consigned to the small retailers. It is a mutually beneficial arrangement for seller and buyer to have a competitive freight rate.