CPT
Carriage paid to (Place of Destination)
Explained
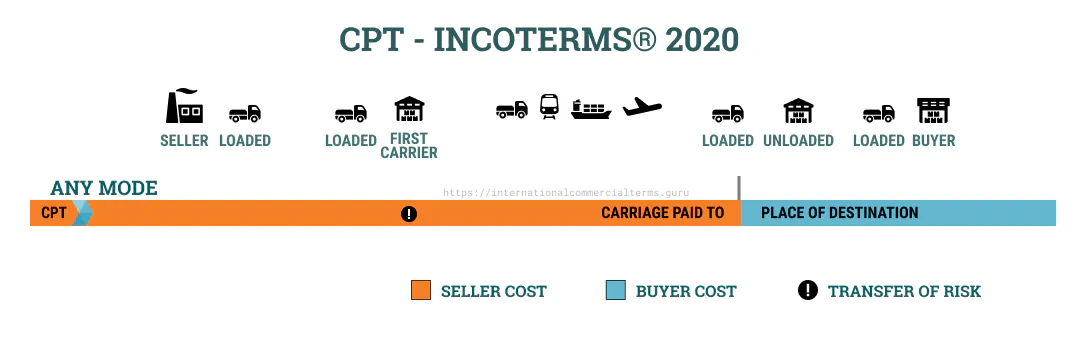
In CPT, the seller clears the goods for export and delivers them to the carrier at the agreed place of shipment. The buyer is now responsible for the goods. The seller is responsible for the main carriage until the agreed destination. The contract must say where the goods are going and where they came from. This term can be used for any mode of transportation.
Mention the destination clearly in the sales contract. Unless otherwise agreed, unloading will be under the seller’s account.
Doing Business
Like CIP, but no insurance paid by the seller. Seller pays for shipping. The buyer gets insurance. The seller pays for freight until the final destination. Delivery happens at the origin with the first carrier. The seller arranges export clearance for any mode of transportation. If there’s a problem, the buyer can claim with the insurance company. There’s no extra cost for transporting freight to the port or inland warehouse. Additional handling charges will apply. The buyer clears customs. If there are delays at the origin, the buyer and seller usually discuss this.
This term is used for Ro-Ro and airfreight shipments. If there are more than one way to ship, the risk is transferred when the goods are delivered to the first carrier.

Examples
Computer monitors from China to Indonesia:
CPT Customer warehouse Jakarta, Indonesia - Incoterms® 2020The seller, a reputable electronics company, sells monitors to Jakarta by ocean. The seller pays for shipping to a warehouse in Jakarta and unloads the goods. The buyer must insure the goods from origin to the Jakarta warehouse. The buyer can arrange transportation from the port to the Jakarta warehouse, but the seller is responsible for this and any related expenses. The buyer also pays customs fees.
Seller and Buyer obligations
| THE SELLER’S OBLIGATIONS | THE BUYER’S OBLIGATIONS |
|---|---|
| A1. General The seller must deliver the goods, commercial invoice, and any evidence of conformity. | B1. General The buyer must pay the price of goods as agreed. |
| A2. Delivery Deliver the goods to the carrier on the agreed date or period. | B2. Taking Delivery The buyer takes the goods from the carrier at the place of destination. |
| A3. Risks All risk of loss/damage until goods have been delivered. | B3. Risks All risk of loss/damage from the time or end of the period agreed for delivery. If the buyer fails to give notice of the port of destination, the risk is under the buyer. |
| A4. Carriage Contract carriage of goods until the place of destination. | B4. Carriage No obligation to contract a carrier. |
| A5. Insurance No obligation insure the goods. | B5. Insurance No obligation to insure the goods. |
| A6. Delivery/transport document Provide the usual transport document and dated within the agreed shipment period. Full set of originals if the document is negotiable. | B6. Delivery/transport document Accepts the proof of delivery |
| A7. Export/Import clearance All export clearance expenses (license, security, inspection, etc). Assist with import clearance | B7. Export/Import clearance Assist with export clearance. Pay for import clearance and formalities (licenses, security, official documentation). |
| A8. Checking The seller must check, count, weight, mark, and package goods | B8. Checking No obligation. |
| A9. Allocation of cost Pay all the cost until delivery, freight cost, loading cost, and unloading. Transit costs. Cost of proof of delivery. Duties and taxes for export. All costs related to providing assistance in obtaining documents to the buyer | B9. Allocation of cost Pay from the time goods delivered. Unloading cost not related to the contract of carriage. All costs for assistance on getting documents and information. Pay duties and taxes for import or transit. Any additional cost if the seller is not notified about shipment date or period. |
| A10. Notices Give notice that goods have been delivered. | B10. Notices Time or period for dispatching the goods and name the point of receiving the goods. |
FAQ about CIP and CPT
Where does risk transfer under CPT/CIP?
Risk transfers when the seller delivers goods to the seller’s carrier (not at the destination).
For containerized shipments (Expert insight from Bob Ronai, member of the Incoterms 2020 Drafting Group):
- FCL: Risk passes when delivery is made to seller’s carrier, usually at seller’s premises. Ocean freight services starting at Door of Seller or services starting at the container yard (CY).
- LCL: Same - typically at seller’s premises
- Even if seller delivers to carrier’s depot, delivery occurs when vehicle arrives ready for unloading, which could be hundreds of kilometers from the actual port. This is usually a warehouse or cargo freight station where cargo is received for loading into containers.
Critical point: Both CPT and CIP fail to clearly explain delivery to the carrier. In practice, delivery works exactly the same as FCA - it can be at seller’s premises or at carrier’s place.
Is the seller responsible for loading costs under CPT/CIP?
Yes, but where matters:
The seller retains risk for CPT and CIP exactly as for FCA. The only difference is:
- FCA: Buyer’s carrier (explained clearly in the rules)
- CPT/CIP: Seller’s carrier (clarity was needed but not provided in Incoterms 2020)
What does “physical possession in the manner appropriate to the means of transport used” mean?
This confusing wording from CPT/CIP Article A2 caused debate even among the Drafting Group members.
What it means in practice: The manner of handing over goods to the carrier depends on the transport mode and type:
- Container at seller’s premises: goods loaded into container
- LCL at seller’s premises: goods loaded onto truck
- At carrier’s depot: goods arrive on seller’s transport ready for carrier to unload